If there’s one industry we all just can’t live and do without, it has got to be the food industry. People just cannot live without eating, and they have to eat; there’s simply no other way around it. For such a vast industry that continues to grow more and more every year, we see that expense reduction or cost containment in food processing plants is still as energetic as ever.
For the majority of food manufacturers and food processing companies, compromising the quality of produce to obtain a lower cost is simply out of the question. As a result, like all the other process industries, food manufacturers are seeking ways to enhance productivity throughout the plant using factory automation.
Automation exists everywhere in contemporary food plants, whether in the packaging or the actual processing of the food. Although most large manufacturers integrate robots and use high-tech automation in the food industry , it still isn’t as popular in small-to-medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Nevertheless, there are many reasons why it should be, and we’re about to see them.
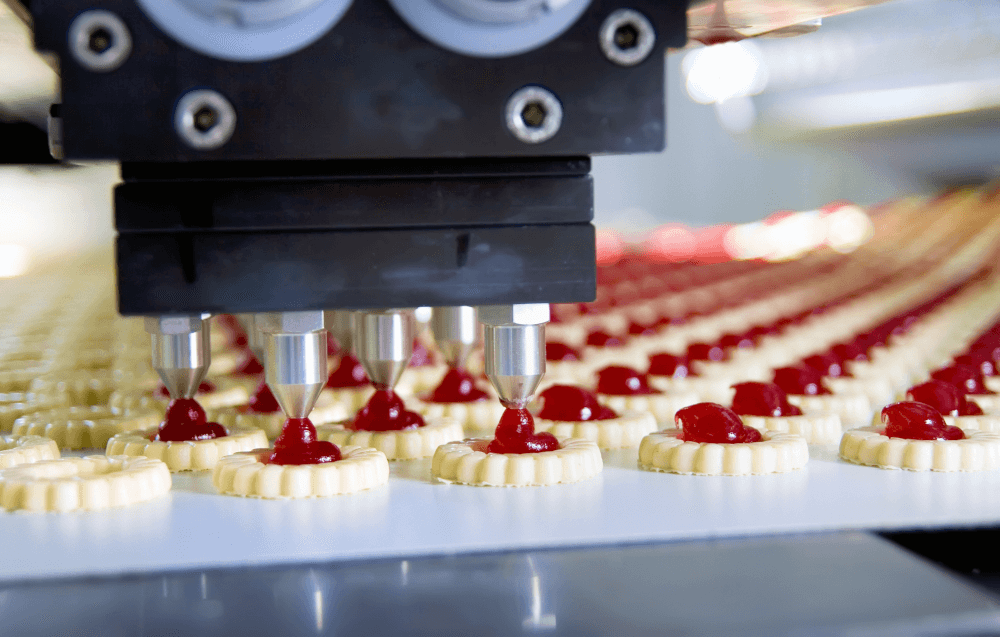
The Rise and Evolution of Automation in the Food Industry
Robots have entirely changed how manufacturing is done in practically every industrial sector and have significantly increased product consistency and efficiency. However, until recently, food manufacturers have been an exception to this spiraling trend.
While there are reasons for this, one of the most commonly cited reasons is that food items significantly differ in terms of shape and consistency. As a result, this raises a considerable degree of challenge to automated processing techniques.
But now, as we look at contemporary food packaging and processing plant, you’ll come across a vast array of different machinery, including:
- Forming and cutting machines
- Automated ovens
- Blending machines and mixers
- Sortation equipment
- Wrapping equipment
- Filling equipment
In addition, there are several robots as a vastly automated automotive assembly line. As per the Association for Advancing Automation and Robotic Industries Association, robotic systems for consumer goods and food manufacturers grew by 56% in 2020.
Now, automation is no longer an option in the food industry but rather a necessity to address the required levels of production speed, quality control, overall profitability, shortage of labor, and overall profitability.
The Food Industry
The food manufacturing industry is incredibly fragmented and diverse, consisting of some of the largest and smallest manufacturers. However, most of them can be categorized as SMBs.
Food assembly and manufacturing are primarily performed manually, particularly more so in SMBs. At present, the larger food manufacturers incorporate automation by integrating robots and state-of-the-art automated industrial machinery.
However, it is not as widespread in small-to-medium-sized businesses, where spending on engineering research and development (R&D) and technical infrastructure is considerably lower. Food retail mainly tends to focus on a small number of key retailers. Consequently, these retailers have a great deal of influence on product pricing and range.
Nevertheless, some of the more fundamental issues most food manufacturers face include intense competition from within and abroad, pressure to minimize costs, shorter lead times, growing demand for a vast assortment of products, environmental legislation, and increasing public awareness of food and hygiene standards.
Current Manufacturing Procedures
The roots of the food manufacturing industry can be found in the household kitchen, as manufacturers prepare food in factory settings that are a larger version of the domestic environment.
With a rise in the production demand, larger companies saw the array of opportunities and plethora of benefits of automation, particularly so for end-of-line palletizing and packaging. Only just, the availability of effective robots enabled automation to move upstream and take on numerous operations with action food products on assembly lines.
In general, smaller companies have been relatively slower in incorporating automation. Some of the reasons for this are high market volatility, limited low-cost labor and expertise, the prevalence of short-term orders, and the belief that automation is unfit for assembling fragile, variable, soft, and sticky/slippery natural products.
These reasons have significantly discouraged small and medium businesses from making capital investments in automation, thus resulting in a strong dependence on manual manufacturing procedures. However, some market and other trends have sprung up over the last decade, seriously challenging the conventional physical-intensive manufacturing approach.
This also includes a decline in the availability of low-cost, suitable casual labor, employment health and law and safety directives that pressurize labor costs, higher commodity prices, and a surge in demand for assured hygienic products, which might indicate elimination of human workers from production processes.
The good news for consumers and the industry alike is that robotics technology and automation have been developing steadily to meet these challenges. Modern-day automation and robotics are more versatile than ever, making them worth adopting for food manufacturing companies of all sizes.
7 Innovations SMBs Can Adopt in 2022
Adding additional machines and labor can undoubtedly help boost volume during seasonal demand peaks in the food industry. Still, it comes with a significant cost, one that you can shave with the adequate process and system updates.
As one might expect, the best solution is to incorporate advanced automation systems and processes that can be controlled via software or machinery. These advanced systems are designed to work together with and enhance the performance of existing teams and laborers.
Innovation is bound to deliver various benefits since it is all about adopting new ways of working and improving your current processes, which can be automated to help companies become more agile.
Most people have a misconception about the idea of automation, thinking automation replaces humans entirely. On the contrary, automation is about running business operations efficiently to reduce human efforts, minimize high labor costs, and enhance worker safety. Instead of replacing people, automation requires new skills from them.
Now, moving on to discussing various applications of cutting-edge modern automation systems in the food industry, the utmost focus is on Industry 4.0 , i.e., the digitization of manufacturing. The digital breakthrough for the food industry rests in the likelihood of gathering and utilizing a wave of production analytics and data.
New and innovative technologies like sensor networks, blockchains, and the Internet of Things will have a significant and disruptive effect on food production. This will allow companies to use the data to monitor the production and account for the sought-after quality and consistency of food.
Having said that, let’s look at 7 innovations small-to-medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can and should adopt in 2022 by integrating robots and automating industrial machinery and processes.
Smart Manufacturing
We all are aware the food industry is now more fast-changing and complex than ever before. Food makers worldwide have to instantly and constantly adapt their products and processes to keep pace with the rapidly changing consumer demands and markets.
Smart manufacturing can be leveraged to back the food industry's efficiency, innovation, and sustainability.
Smart manufacturing utilizes the data to generate a single view of operations that facilitates communication amid assets, data, and people. This indicates that when new challenges come upon, food manufacturers can easily avoid downtime and optimize processes now in the most unimaginative ways.
By incorporating smart manufacturing, data can be leveraged to unlock tremendous productivity gains and enhance competitiveness, effectively shining a light in specific areas that food makers would’ve been edgy to identify.
Smart machines and smart manufacturing enable food manufacturers to add flexibility and agility into their production processes as well as drive resource efficiency.
Robots/Cobots
Robots and cobots (a.k.a, collaborative robots) have slowly made their way into the food industry over time. This entirely new generation of robots is designed to interact and work together collaboratively with humans.
Regardless of the many benefits flaunted by cobots, the food manufacturers typically hesitate to integrate automation within their assembly lines, primarily because of the fallacy that robots are only suitable for large-scale operations and call for significant capital investments.
However, unlike conventional industrial robots, which are enclosed, bulky, and dangerous, collaborative robots are incredibly lightweight, small. Besides, they don’t need any physical safety barriers.
You can easily integrate cobots into manufacturing lines in most settings. Here are some ways food manufacturers can profoundly benefit from cobots:
- Taking over mundane and repetitive tasks.
- Increased efficiency and productivity.
- A better and safer work environment.
- Manufacturing flexibility.
Thanks to the significant advancements in vision and sensor technology, robots can now successfully operate alongside humans without physical barriers. It is vital to stay relevant, competitive, and up to date in the food industry, which is volatile and fast-moving.
As the food industry is taking steps towards greater use of automation, cobots can likely be the key and foreseeable future of food manufacturing. This is something SMBs in the food industry worldwide should take advantage of.
Lot Traceability
Food manufacturers heavily rely on their consumers’ faith that the food they consume is safe and free of contamination. Most food businesses deem living up to such high consumer expectations a solemn pledge and duty, so they take the necessary steps to fulfill their promise.
In addition to being delicious and nutritious, their products must be worth the trust. The production methods should comply with federal laws, such as the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act. Lot traceability in ERP systems is one of the best and most effective ways to meet these expectations.
It ensures safety and quality
Consumers take a keen interest in knowing the origins of their food ingredients. The rising popularity of the “Farm to Table” movement and limited ingredient goods precisely demonstrates that.
Using food lot traceability , food makers can understand where each ingredient came from precisely and then verify if it meets the quality specifications. The increased visibility into these sources helps consumers and manufacturers feel more confident that the food they consume was created with utmost care and meets all the necessary safety and quality standards.
It prevents counterfeiting
Using lot tracing and tracking, food manufacturers can verify that consumers are met with only authentic goods. Even if counterfeit products end up on the shelves of stores, lot tracing and tracking pinpoint the exact location where they entered the supply chain. This way, manufacturers can take the necessary steps to prevent such issues from occurring in the future.
It helps manage recall costs
Despite their best intentions, most food makers are required to occasionally recall their products due to issues with a particular ingredient or a problem that occurred during a specific time in the manufacturing process.
Lot tracing and tracking is a highly effective tool for managing recalls. By knowing the affected lots, manufacturers can track them to the distribution or retail centers. This helps to significantly limit the cost and scope of any required calls.
It prevents damage to your brand
Recalls, adulteration, and counterfeit products are some of the worst ways consumers’ trust in your brand can be eroded. An ERP system that incorporates effective lot tracing and tracking capabilities can significantly prevent harm to your brand by verifying the purity and quality of the ingredients you use, along with all that you produce.
The Internet of Things
IoT , short for the Internet of Things, basically refers to the network of devices that collect and convey information through the internet. The food industry is slowly but surely getting accustomed to IoT.
With the vast number of extraordinary IoT applications, the food processors, suppliers, and retailers are experiencing an array of excellent opportunities for operational and financial escalation in their respective food businesses. Undoubtedly, the food industry can run to its maximum potential by adopting the Internet of Things, and for good reasons.
For instance, IoT is significantly helping companies to achieve the highest levels of food protection, minimize wastage, improve traceability, and mitigate risks and costs across the many different food processing and packaging stages.
Each functional area of the food sector has gotten significantly better since they integrated IoT. This is because it facilitates food companies to ensure and provide maximum food safety, superior levels of traceability, and ultimately accountability through the farm-to-table supplies chain operations.
Besides this, there is an endless list of benefits offered by the Internet of Things technology in the food industry. As a result, the impact is also quite impressive.
Automated Storage/Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Customer trust and satisfaction are two of the most essential constituents of the food industry. Food distributors and manufacturers' refining operations depend on optimum product quality, reliability, and freshness to stay on top of the market and competition.
Food safety is a massive challenge for most distributors and manufacturers in warehouses. Hence, the need to alleviate product recalls, and their damaging effects is more crucial now than ever. Consequently, most companies are turning to automation for good.
An automated storage and retrieval system (AS/RS) is one of the principal technologies making ripples to minimize (if not wholly prevent) recalls via the use of real-time inventory insights. AS/RS’s high-speed nature escalates how manufacturers and distributors move the products in and out of the warehouse, thus averting wastage.
In addition to safeguarding brand reputation and safety, automated food warehousing offers numerous long-term benefits to the warehouse operations in general – from decreasing inventory inaccuracies and minimizing costs to optimizing the flow of materials and boosting productivity.
As the number of industry laws and regulations continues to rise due to product recalls, it is entirely up to food businesses to take matters into their own hands and invest in automation technology to keep their brands intact and consumers safe.
Predictive Maintenance
While the food industry clearly does not pose any threats to the environment, it can certainly have a devastating impact on our health. From strict regulatory standards to complex equipment, the food industry has to confront maintenance challenges.
For instance, broken equipment can result in significant health concerns down the line. It can completely tarnish and destroy a company’s reputation, and in the worst-case scenario, the breakdown of equipment can even lead to spoiling and wastage of foods, which might be mixed with the batch of fresh foods when delivered to consumers.
The only way to prevent these risks associated with our health is to have an entirely stable and controlled environment for the safety and storage of perishable products. This is precisely where predictive maintenance takes the stage.
Predictive maintenance is a high-impact strategy plan as it is centered on forecasting issues before they actually occur. With the help of predictive analytics software and sensors, fault(s) in equipment can be foreseen before they occur, giving maintenance teams the essential data they need to avert breakdowns long before they can happen.
Abiding by the most strict laws on food items can be incredibly challenging. However, with the proper observation of critical equipment, there is a significantly lesser chance that something out of the blue might happen. This is especially the case when predictive technology is combined with proactive maintenance techniques and CMMS software.
Some of the advantages of predictive maintenance include:
- Improved root cause analysis
- Improved uptime
- Less time spent on inspections
- Regulatory compliance
- Cost savings over time-based preventive maintenance
- Higher quality product output
- Higher efficiency
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
While the food industry hasn’t been the most responsive to technology in these few years, Artificial intelligence is bound to be the catalyst for bringing in this breakthrough. It simply isn’t a question anymore if AI will observe more meaningful use in the food industry. Instead, it is now a question of how swiftly and significantly it is catching up in the food industry.
In 2020, AI in the food industry was valued at a striking $3.07 billion and was projected to reach a whopping $29.94 billion by 2026 at a compound annual growth rate of 45.77%! The evolving consumer need for affordable, quick, high-quality, nutritional, and easily accessible food options have led to these changes. Here are 10 applications of artificial intelligence in the food industry:
- Sorting Fresh Produce
- Developing New Products
- Streamlining the Supply Chain
- Cleaning processing equipment
- Maintaining Food Safety Compliance
- Higher Quality Food
- Consumer’s Choice
- Virtual Assistants
- Streamlining Business Operations
- Self-Ordering
The Future of Automation in the Food Industry
As we look into the future, food manufacturing processes will most likely remain the same. However, the bias against automation has significantly died out. The only difference is that you can expect to see a swift adoption of novel sensor-enabled automated equipment across large and small-to-medium-sizes businesses.
Manual operations will possibly continue for some products and markets, but this too will be scattered with bits of apt automation. In general, the nature and shape of the food industry will be controlled by market forces.
However, the automation industry has a vital role to play by providing technology that’ll make sure the food sector continues to meet the high demand for high-quality, readily available, and reasonably priced food products.
A significant challenge the food industry encounters in integrating robots and implementing automation is seeking enough engineers to support the adoption of cutting-edge manufacturing techniques. Hence, schools, professional engineering institutes, and training centers also have a huge role in creating a genuine food manufacturing industry.
Wrapping Up
Food manufacturers, both large and small/medium-sized, are aware of today and tomorrow’s challenges. As a result, they are focused on developing innovative and new products to automate every process along the way.
By incorporating these innovations into their manufacturing processes and operations, small-to-medium-sized food manufacturers can profoundly benefit from enhanced end-to-end traceability, better quality control, increased efficiency, improved worker safety, brand protection, and increased flexibility.
The jobs in food processing might gradually shift from manual labor, where laborers sit on the side of conveyors sorting, picking, and packaging food items, to operators who oversee all the processors in the back of a control room while keeping a vigilant eye on equipment efficiency, speed, and quality control.
However, there is one thing; the food industry isn’t one to run in the dark. Hence, it’ll always need some kind of human intervention.




